Activities for the development of genomic medicine in biliary tract cancer

Chigusa Morizane
2023/7/15
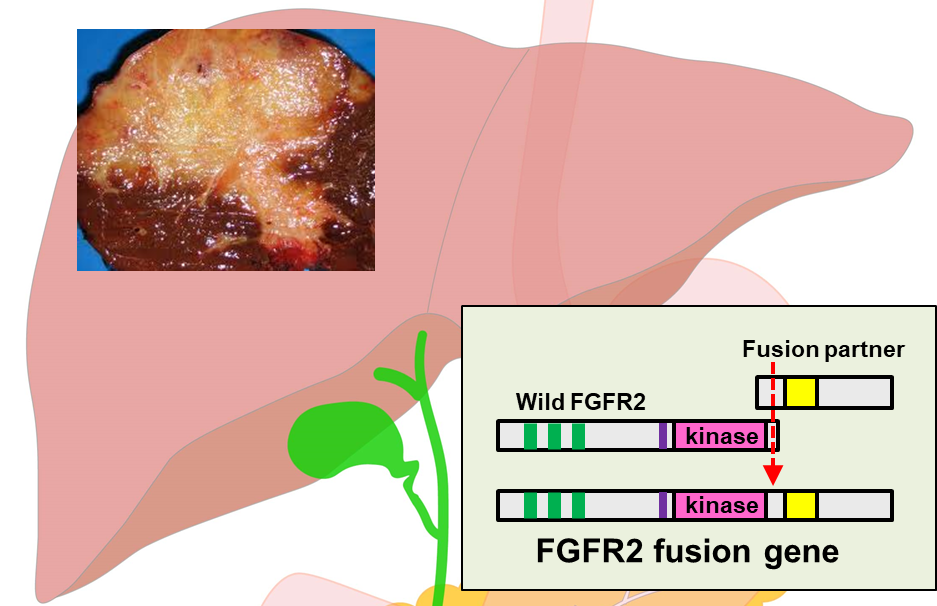
Biliary tract cancer (BTC), with a high incidence in the Asian countries, is an intractable cancer and effective drug therapies have been limited. However, several genetic abnormalities have been reported as potential therapeutic targets in recent years. One of the most promising targets, the FGFR2 fusion gene, was discovered through basic research at the National Cancer Center Research Institute (Hepatology. 2014; 59(4): 1427-1434). To apply this discovery to clinical practice, the National Cancer Center Hospital have conducted a multicenter prospective observational study (PRELUDE Study) which enrolled more than 400 advanced Japanese BTC patients and investigated the frequency and characteristics of FGFR2 fusion gene positive patients (J Gastroenterol. 2021 Mar;56(3):250-260.). Furthermore, we have initiated and conducting the CHOICE study, an international collaborative study of FGFR2 fusion genes in BTC with expansion to Asian countries.