For patients and health care professionals
Why is A-TRAIN being conducted in Asia?
- QWhat is the difference between cancer patients in Asia and Western countries?
- ACancer types that are more frequent differ between Asian and Western countries due to differences in lifestyle, environmental factors, etc. In Asia, cancer is often caused by infection, smoking, and alcohol consumption. In addition, there are differences from Western countries in histology, age, etc. of affected patients, even for the same cancer type.
Source: Ahmedin Jemal, et al (2019). The cancer atlas, third edition, The American Cancer Society, Inc.
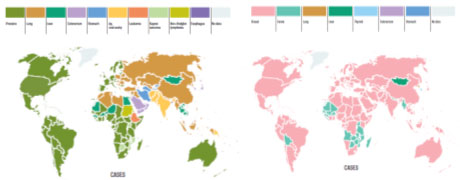
- QWhat kinds of cancers are characteristic of Asia?
- AIn Asia, the rates of stomach and liver cancer are higher than in Western countries. Additionally, oral and nasopharyngeal cancers are reported to be more common in men, and cervical cancer is more common in women. It is known that infectious diseases are deeply involved as one of the causes of these cancers.*
Additionally, when it comes to ovarian cancer, clear cell carcinoma accounts for 4–12% of all ovarian cancers in the West and 10–20% in Asia. Patients with breast cancer tend to be younger at the time of diagnosis in Asia, and there are more cases of Luminal B than in the West.Types of cancer Cause Stomach cancer Helicobacter pylori Liver cancer HBV/HCV Nasopharyngeal cancer EBV Cervical cancer HPV (human papillomavirus) Bile duct cancer Clonorchis sinensis, bacterial infection, HBV/HCV Oral cancer Chewing tobacco2 - QWhat is the significance of conducting joint research in Asia?
- ACancer types that are more frequent in Asian and Western countries differ. Therefore, it is difficult to satisfy unmet medical needs in Asia through clinical trials and clinical studies that are mainly conducted in Western countries. It is believed that A-TRAIN will provide support within Asia to deal with cancer types that are common in Asia. In addition, carrying out research by collaborating with multiple countries will allow us to collect more cases quickly and accelerate our research.
- QWhy is Japan taking leadership?
- AJapanese cancers also share some similarities with Asian cancers, and it is likely that we will discover features including target molecules and genetic mutations that have not been found in data from Western countries. Additionally, it is believed that cooperation with Asia will enable us to overcome cancer types that have not been studied in Japan alone due to the small number of cases, thereby accelerating the development of therapeutic drugs.
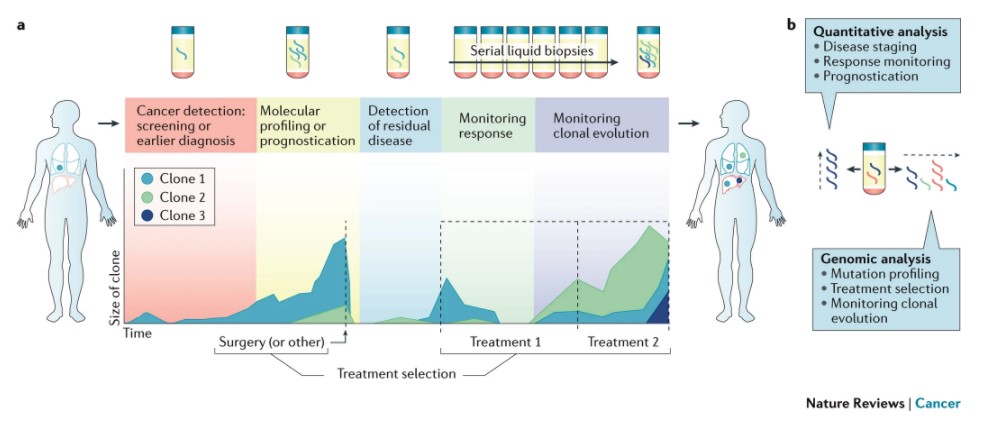
What is a liquid biopsy?
【Overview】
This is a generic term for techniques that use blood or body fluids to diagnose and measure biomarkers. Tumor-derived DNA circulated in blood (circulating tumor DNA: ctDNA) analysis is the most advanced in clinical application at this time. In the future, various clinical applications are expected, such as early diagnosis of cancer and monitoring for recurrence, search for therapeutic targets, and prediction of efficacy after treatment.
Source: Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology volume 18, pages297–312 (2021)
【Q&A】
- QWhat kind of problems have been encountered with conventional tumor tissue collection?
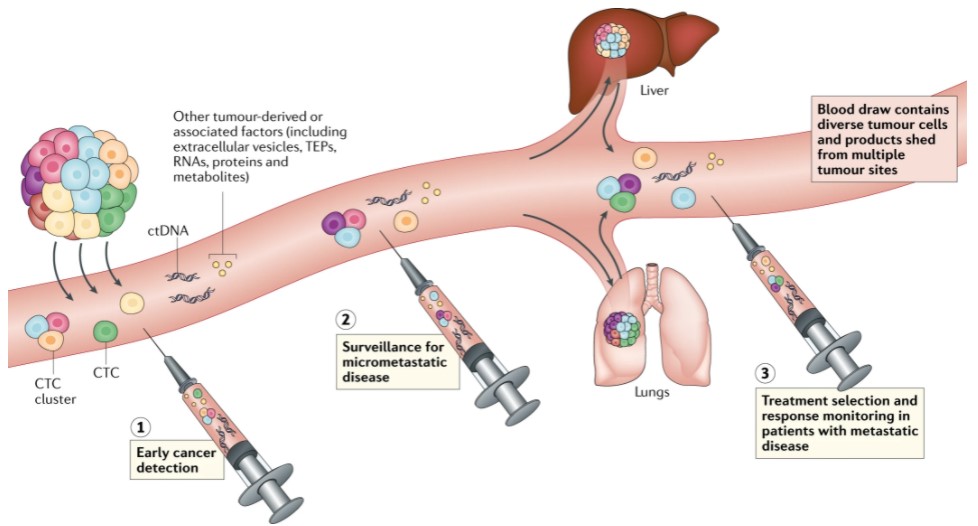
- AIn the past, analysis of biomarkers, such as oncogenes, required the collection of tumor tissue through biopsy or surgery. Tumor tissue collection is very burdensome to the body, whereas a liquid biopsy can collect tumor-derived material from blood samples or urine.
- QWhat is the benefit of being able to collect specimens from blood or urine?
- ASince it does not involve major invasive procedures such as biopsy or surgery, specimens can be collected with less burden on the patient. Thus, genetic mutation can be analyzed even if biopsy or surgery is difficult. Furthermore, it can be implemented multiple times. Finally, a key feature is that results are returned more quickly than with tissue specimens.
- QHow useful is it to be able to analyze quickly and repeatedly with low invasiveness?
- ABy using blood and urine samples, it is possible to evaluate genetic mutations in an entire tumor, including metastatic lesions, in real time. It is important to obtain real-time genetic information because genetic mutations in cancer are known to change over time, including at recurrence and during progression. Furthermore, repeated evaluations can also be used to monitor the degree of progression of a disease.
- QHow are genetic mutations detected in collected blood samples?
- ADNA fragments free in plasma from which blood cell components have been removed are examined.
- QAre there any disadvantages associated with using samples from blood or urine compared to tissue samples?
- A If some tumors with a slow growth rate or low tumor volume are tested, a false negative result may be obtained due to insufficient gene dosage.
Source: Nature Reviews Cancer volume 17, pages 223–238 (2017)